Curriculum
Science
The Subject Way
Firstly, to teach students the vital skills they need to achieve their full potential and gain the very best grades they can. Secondly, to teach students how each subject relates to the wider world, incorporating the life skills they will learn.
It is our belief that knowing how what you learn links to the wider world brings a subject to life and therefore improves overall understanding and engagement.
Why study Science?
Science affects your life in many ways – the clothes you wear may include man-made fibres, the food you eat may contain chemical colourings, household appliances contain electric circuits.
Our Science course encourages you to acquire a body of scientific knowledge and develop an understanding of Science including its power and limitations; develop experimental and investigative abilities; develop an understanding of the nature of scientific ideas and activity and the basis for environmental applications of Science and of the economic and social implications of these.
What will I learn about?
An equal amount of Biology, Chemistry and Physics are studied in all Science courses.
You will develop an understanding of how Science works and learn how to use scientific evidence to answer questions such as:
- What the possible risks are of giving children vaccinations?
- When is it economical to extract metals from their ores?
- How can radioactive tracers be used to detect forged bank notes?
To do this you will develop and improve your scientific communication skills by using different approaches to presenting information including using the Internet.
How will I be assessed?
6 Exams in Year 11 in GCSE Combined Science (Trilogy)
The GCSE course begins to be taught in Y9. Students will study Combined Science. In this course, students study the three sciences of Biology, Chemistry and Physics, and are assessed through 6 exams in Year 11. Students leave school with two GCSEs in Science.
What do employers think about the subject?
For many careers, good Science qualifications are essential.
These include careers such as Nursing and Health Care, Child Development, Engineering, Architecture and Construction, Surveying and any other careers that have a technical aspect.
Employers at all levels see Science as a desirable qualification, as it shows that students are able to demonstrate a wide variety of skills essential in the workplace, such as analysis and interpreting data, applying knowledge and researching.
What are the skills I will gain?
In Science you will develop your ability to:
- Plan strategies to develop and test ideas
- Select, organise and present information clearly and logically
- Analyse critical data using knowledge and understanding
- Use ethical, moral, social and economic reasons to explain your ideas
Year -by-Year Subject Breakdown
Biology
Focus – Cells and Systems U1
Content
Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and microscopes allow detailed comparisons of plant, animal, and unicellular organisms. Specialised cells carry out particular functions, and the skeleton, muscles, and joints work together to support the body, protect organs, and enable movement.
KEY VOCABULARY
Cell, Microscope, Magnification, Nucleus, Specialised Cell, Skeleton, Muscle
Chemistry
Focus – Particle Model U2
Content
The particle model explains how all substances are made of tiny particles, and their arrangement and movement describe the differences between solids, liquids, and gases. Heating and cooling change particle energy, leading to changes of state, while melting and boiling points, diffusion, gas pressure, and purity help explain how substances behave in different conditions.
KEY VOCABULARY
Particle, Solid, Liquid, Gas, Diffusion, Gas Pressure, Pure Substance
Physics
Focus – Forces and Motion U3
Content
Forces can change the motion of objects, shown through force diagrams and the turning effect of moments. Speed describes how fast something travels, represented on distance-time graphs, and pressure explains how forces act over an area in solids, liquids, and gases.
KEY VOCABULARY
Force, Resultant Force, Moment, Speed, Distance–Time Graph, Pressure, Fluid Pressure
Biology
Focus – Reproduction and Variation U4
Content
Variation explains why individuals differ, and human reproductive processes,including the menstrual cycle, fertilisation, and foetal development show how new life begins. Plants also reproduce through pollination, fertilisation, and seed dispersal, allowing them to spread and survive.
KEY VOCABULARY
Variation, Fertilisation, Menstrual Cycle, Gamete, Foetus, Pollination, Seed Dispersal
Chemistry
Focus – Atoms, Elements and Mixtures U5
Content
Atoms are the building blocks of all substances, forming elements, compounds, and mixtures with different properties. Chemical formulae describe how atoms combine, and mixtures can be separated using techniques such as dissolving, filtration, crystallisation, distillation, and chromatography.
KEY VOCABULARY
Atom, Element, Compound, Mixture, Filtration, Distillation, Chromatography
Physics
Focus – Energy U6
Content
Energy exists in different stores and transfers between them in predictable pathways, with the total always conserved. Power and the cost of electricity show how energy is used, while efficiency, conduction, convection, infrared radiation, and energy resources explain how energy is transferred, lost, and supplied.
KEY VOCABULARY
Energy Store, Energy Transfer, Conservation, Power, Efficiency, Conduction, Renewable Resource
Physics
Focus – Waves U7
Content
Waves transfer energy without transferring matter, and their behaviour explains how we observe the world. Light waves reflect, refract, and separate into colours, allowing the eye to form images, while sound waves travel as vibrations through different materials and have practical applications in communication and technology.
KEY VOCABULARY
Wave, Reflection, Refraction, Frequency, Amplitude, Light, Sound
Chemistry
Focus – Acids and Alkalis U8
Content
Acids and alkalis have characteristic properties identified using indicators, and the pH scale shows how strong or weak they are. Neutralisation reactions, including those with metals and carbonates, form useful products, and crystallisation techniques allow salts to be made and purified.
KEY VOCABULARY
Acid, Alkali, pH, Indicator, Neutralisation, Salt, Crystals
Biology
Focus – Organ Systems U9
Content
A healthy diet provides the nutrients needed for the body to function, while deficiencies can lead to specific health problems. Digestion breaks food into smaller molecules for absorption, and the breathing system works closely with aerobic and anaerobic respiration to release energy for the body.
KEY VOCABULARY
Digestion, Enzyme, Absorption, Breathing System, Aerobic Respiration, Anaerobic Respiration, Nutrient
Physics
Focus – Matter U10
Content
The particle model explains how the arrangement and movement of particles link to the properties of solids, liquids, and gases. Changes of state, diffusion, energy in matter, and why objects float or sink can all be understood by considering the spacing, movement, and interactions between particles.
KEY VOCABULARY
Particle, State, Density, Diffusion, Energy, Solid, Liquid, Gas
Chemistry
Focus – Reactions and energy changes (U11)
Content
Chemical and physical changes can be distinguished by whether new substances form, and elements and compounds react in predictable ways. Conservation of mass underpins all reactions, including oxidation, reduction, displacement reactions, and exothermic and endothermic changes, each with characteristic energy profiles.
KEY VOCABULARY
Reactant, Product, Conservation, Oxidation, Reduction, Exothermic, Endothermic
Biology
Focus – Plants and Photosynthesis U12
Content
Photosynthesis allows plants to make their own food, supported by key leaf adaptations that aid gas exchange and light absorption. Factors such as light intensity affect the rate of photosynthesis, and plants form the basis of food chains, passing energy through ecosystems.
KEY VOCABULARY
Photosynthesis, Chlorophyll, Stomata, Diffusion, Adaptation, Producer, Food Chain
Chemistry
Focus – Earths Resources U13
Content
Earth’s structure and the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks link to processes such as weathering, erosion, and the rock cycle. Human activities affect resources, carbon emissions, combustion, the atmosphere, and the greenhouse effect, influencing climate and sustainability.
KEY VOCABULARY
Rock Cycle, Weathering, Erosion, Carbon Cycle, Combustion, Atmosphere, Greenhouse Effect
Biology
Focus – Biodiversity U14
Content
Ecosystems contain a wide variety of organisms, and sampling methods help measure how they are distributed across habitats. Biodiversity is essential for stable environments, but it can be threatened by bioaccumulation, habitat loss, and other human impacts, leading to conservation challenges and potential extinction.
KEY VOCABULARY
Sampling, Ecosystem, Habitat, Biodiversity, Bioaccumulation, Conservation, Extinction
Physics
Focus – Electricity and Magnetism U15
Content
Electricity flows through circuits, with current, voltage, and resistance determining how components behave and how energy is transferred. Magnetic fields are produced by permanent magnets and electromagnets, explaining how forces act in devices and technologies that rely on magnetism..
KEY VOCABULARY
Current, Voltage, Resistance, Circuit, Magnet, Electromagnet, Field
Chemistry
Focus – Atomic Structure & Periodic Table U16
Content
Atoms contain protons, neutrons and electrons arranged in shells, and different models explain how scientific understanding has developed. The periodic table groups elements by similar properties, with patterns in reactivity and trends shown across groups, including metals, non-metals, and specific families such as Group 1 and Group 7.
KEY VOCABULARY
Atom, Proton, Neutron, Electron, Periodic Table, Group, Reactivity
Biology
Focus – Genetics and Evolution U17
Content
DNA, genes, and chromosomes carry information passed from parents to offspring, shown through inheritance patterns and family trees. Adaptations affect survival, predator–prey relationships shape ecosystems, and natural selection drives evolution, supported by fossil evidence and applied in selective breeding and genetic modification.
KEY VOCABULARY
DNA, Gene, Chromosome, Inheritance, Adaptation, Natural Selection, Evolution
Physics
Focus – Space and Forces in the Universe U18
Content
Gravity acts throughout the universe, affecting objects on Earth and other planets, and explains orbital motion of moons, satellites, and planets. The solar system’s structure links to seasons, day length, and the wider universe of stars and galaxies.
KEY VOCABULARY
Gravity, Orbit, Planet, Star, Galaxy, Satellite, Solar System
Biology
Focus – The Human Body and Disease U19
Content
Pathogens cause infectious disease, and factors affect how quickly microorganisms grow and spread. The body uses a range of defences, including the immune system and vaccines, while hormones and the nervous system regulate internal conditions and control responses such as glucose levels and reaction times.
KEY VOCABULARY
Pathogen, Immune Response, Vaccine, Hormone, Nervous System, Reflex, Homeostasis
In Year 10 your child will study:
• Bioenergetics
• Homeostasis and Response
• Inheritance
• Chemical Changes
• Energy Changes
• Rate and extent of chemical change
• Organic Chemistry
• Atomic Structure
• Forces
• Waves
Your child’s progress will be assessed using in-class quizzes and tests, summative assessments at the end of each half term and a mock exam at the end of the year, which will test everything they have learnt throughout Year 10.
Typical homework your child might get in Year 10 is:
• Online quizzes
• Short and longer exam-style questions
• Revision activities, e.g. making note cards on specific topics
In Year 11 your child will study:
In Year 11 your child will study:
• Ecology
• Chemical Analysis
• Chemistry of the Atmosphere
• Using Resources
• Magnetism
Your child’s progress will be assessed using in-class quizzes and tests, summative assessments at the end of each half term and mock exams at two set points during the year, which will test everything they have learnt throughout Year 11.
Typical homework your child might get in Year 11 is:
• Online quizzes
• Short and longer exam-style questions
• Revision activities, e.g. making note cards on specific topics
Head of Department
A Curtis
- a.curtis@thrybergh.com
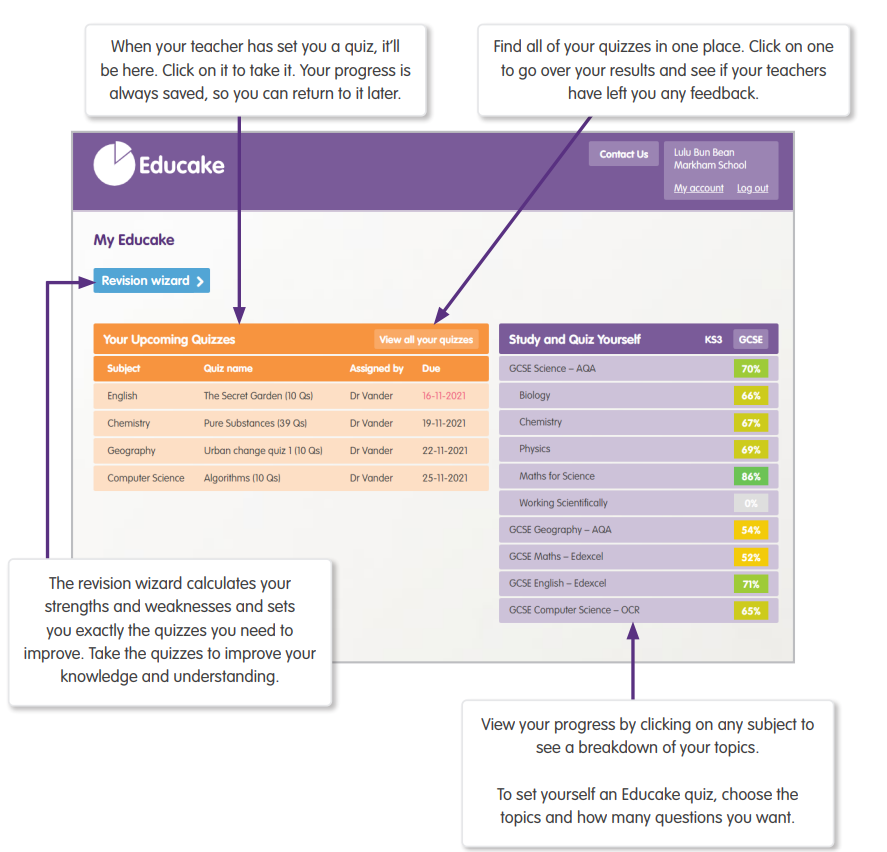
Educake
What is Educake?
Educake is an online learning system for schools. Pupils can use it on a PC, tablet or smartphone by going to www.educake.co.uk.
Teachers might set quizzes on Educake for classwork or for practice at home. Quizzes can be retaken as many times as pupils want to improve their score. Every question is auto-marked, and pupils get instant feedback. Educake is all about progress and positivity.
Pupils also have the opportunity to learn independently. The “Practice” button shows them which topics they need to work on and creates personalised quizzes for them.
Educake Student Video
Educake Parent & Carer Information
Here’s a short video that gives parents & carers a quick overview of Educake.
Find out more
If you would like more information about our curriculum, please contact the school using the details on our contact page.
Our Subjects
CORE SUBJECTS
OPTION SUBJECTS